Page 182 - The-5th-MCAIT2021-eProceeding
P. 182
Step -1: Convert each character in plaintext to their equivalent ASCII value (example: character A equals
65 in ASCII).
Step -2: Convert each ASCII value into binary format (example: 65 in ASCII equals 01000001 in binary).
Step -3: Convert every two binary values to one DNA character (either A, C, G, or T) based on table 1
(example: 00 in binary equals A as DNA character).
Table 1. Binary to DNA table
Binary DNA
00 A
01 C
10 G
11 T
Step -4: Convert each DNA character to their complementary DNA character. Every A character is replaced
with T and vice versa. Every C character is replaced with G and vice versa (example: the complementary DNA
for character A equals T).
Step -5: Convert each DNA character to their equivalent RNA character. The only change is by converting
a DNA character that equal to T to its equivalent RNA character that equal to U (example: the RNA for character
T is equal to U).
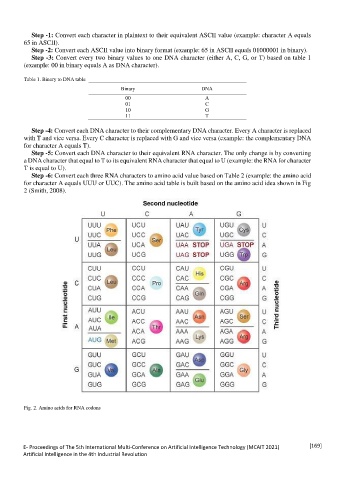
Step -6: Convert each three RNA characters to amino acid value based on Table 2 (example: the amino acid
for character A equals UUU or UUC). The amino acid table is built based on the amino acid idea shown in Fig
2 (Smith, 2008).
Fig. 2. Amino acids for RNA codons
E- Proceedings of The 5th International Multi-Conference on Artificial Intelligence Technology (MCAIT 2021) [169]
Artificial Intelligence in the 4th Industrial Revolution