What is Apel.Q
Accreditation of Prior Experiential Learning (APEL) is a systematic process that involves the identification, documentation and evaluation of learning based on prior experience. Candidates are eligible to be awarded academic qualifications based on knowledge assessment methods obtained from formal education, work experience, life experience or/and a collection of short courses.
Mode of Study
- APEL.Q
Duration of Study
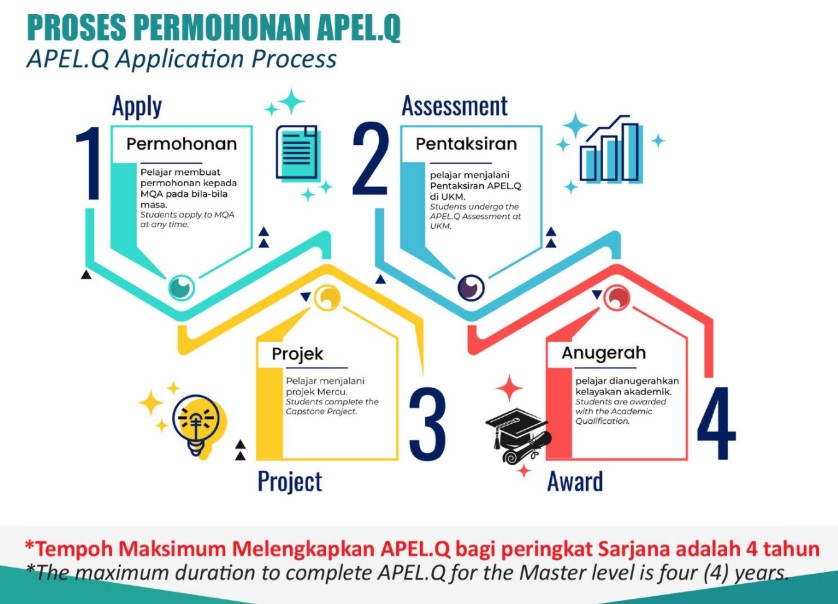
- The minimum duration to complete Apel Q for the Master level is one (1) year and the maximum is four (4) years.

APEL.Q Application Process
- Apply
Students apply to MQA at any time
Individuals with a period of relevant work experience (around 20 years) are eligible to apply field
Open to all (local and International)
- ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL CANDIDATES
- Cyber Security experts from recognized institution resides in Malaysia.
- Alumni of UKM PhD computing students resides in the same country with the candidate.
- Cyber Security top managers from government body of the candidate’s country.
- Cyber Security experts or academics that has collaboration with the faculty members.
- Top management of UKM Pesisir Jakarta office or UKM Qatar office.
- Management of Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
- Assessment
Students undergo the APEL.Q Assessment at UKM - Project
Students complete the Capstone Course - Award
Students are awarded with the Academic Qualification
- When applying, please provide REFERRAL LETTER from one of the following list:
The referral letter is a minimal attestation about candidate formal education and current working background.
- During registration, please provide CERTIFICATE OF GOOD CONDUCT. The certificate (or letter) can be obtain from your:
- 1. Ministry of Foreign Affairs, or
- 2. Police department
Programme Structure
Learning Outcomes
The programme is designed to produce graduates who will be able to:
- Integrate advanced knowledge related to the field of Cyber Security
- Produce innovative solutions related to the field of Cyber Security
- Develop solutions related to the field of Cyber Security using appropriate tools
- Interact effectively through various discussions related to the field of Cyber Security
- Communicate effectively through the publication and presentation of technical materials related to the field of Cyber Security
- Apply numerical skills appropriately in solving problems related to Cyber Security
- Select appropriate digital technologies in solving problems related to the field of Cyber Security
- Demonstrate leadership, teamwork, autonomy, and accountability in delivering tasks
- Show the ability to generate ideas and entrepreneurial thinking in the field of Cyber Security
- Display behavior consistent with professional, ethical, and social considerations
- Prove the ability to expand knowledge related to the field of Cyber Security
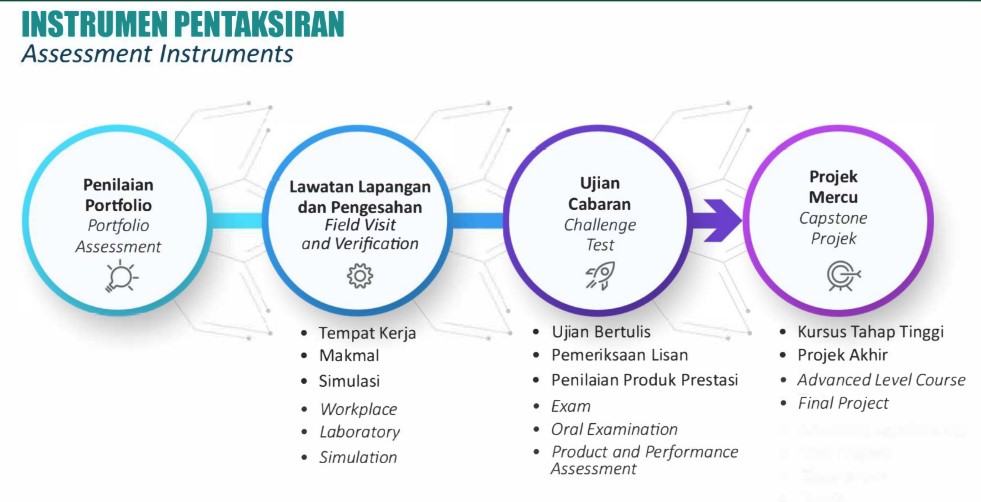
ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENTS
- Portfolio Assessment
- Field Visit and Verification
- Challenge Test
- Capstone Project
During the programme, Apel.Q students can join courses offered by the faculty (or provided by external institutions) to equip their cyber security knowledge. This requirement will be decided by the Apel.Q committee of the programme.
BODY OF KNOWLEDGE
| STRUCTURE | COURSE | |
|---|---|---|
| Core Knowledge |
|
|
| Specific Knowledge (but not limited to the following) |
Platform Security Track | |
|
Digital Forensics Track |
||
|
Financial Technology Security Track |
||
List of Courses
Computer Security [TX6114]
This course presents the basic paradigms and principles of computer security technology and mechanism in modern computer systems. At the end of this course, students should be able to treat computer security problems in a structured way. The course has been structured so that the formal prerequisites only require a minimal knowledge in computer science and mathematics. It is designed to serve as a general introduction to the following topic: computer security fundamentals, security models, cryptography and security issues related to these topics.
Network Security [TX6124]
This course covers the basic and intermediate topics in network security. The aim of this course is to prepare students with the concept and knowledge of using network security protocols and applications to provide security over networks and the Internet. Topics covered include the low level frame packet analysis, analyze each layer in TCP/IP (and the equivalent OSI layer) protocol, as well as the possible threats that come in each layer, network security design, email security, web security, wireless security, and honeypot. Hence the use of important network security tools and applications are introduced such in the lab sessions. The course will also look into vulnerabilities of existing network protocols and the way to overcome them. Students are required to accomplish hands-on lab exercises, practical security assessment as problem-based learning and /report assignments.
Cyber Law and Ethics [TX6134]
This course analyses the phenomena of cybercrime, legal, and investigation/evidential issues, to enable students to relate the evolution of criminal behaviour in parallel with the advancement of technology. Such knowledge would make students always incalculate the culture of cyber security and ethics. Moreover, the course aims to equip students with knowledge on criminal behaviour and social engineering towards mitigating the risk of cyber threats apart from preparing the students as the planner for computer related activities emphasising or ethics, conventions, and laws. On the whole, the course is geared at producing manpower who will serve as reference in matters pertaining to the organisation, initiation, monitoring and supervision of cyber security acculturation and ethics continuously.
Information Security Management [TX6144]
This course includes an overview of conceptual and practical approach to information security management. It focuses on risk management, business continuity management and incident management. Students are firstly introduced to the basic concepts of information security and its management. Later, students are exposed to specific methods, techniques and standards for risk assessment as well as business impact analysis practically. Students are given the opportunity to apply the acquire
Research Method in Computing [TM6114]
This course helps students understand the ethical aspects and techniques of conducting good research. As well as incorporating the elements of technopreneurship and innovation in the research and the relationship of these two elements with the entrepreneurial element. Various types of research approaches and methodologies: developmental, algorithmic, empirical and formal research, are implemented in this course. Training in analyzing literature is among the tasks given to students as well as exposing them to data analysis methods through qualitative and quantitative approaches. The training provided will stimulate critical thinking in the literature review, data analysis and writing of academic research proposals. Students also need to integrate the skills learned and prepare a proposal presentation. Students are taught how to develop research capabilities through creativity and innovation in their minds. Students are also taught to be competitive technologists by linking academic research and business innovation.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention [TX6224]
This course covers the fundamental concepts and design implications required to develop and implement intrusion detection and prevention systems that address security violations in computer systems. The course explains how to detect and prevent unauthorized accesses of networked computers and minimize the damage intruders can do. It emphasizes on techniques and methods for recognizing and handling attacks both automatically and manually. The case studies, large and/or small scales will be covered in this course. Topics to be covered include: main classes of attacks against computer systems, taxonomy and architecture of intrusion detection and prevention systems, network traffic analysis and feature extraction for intrusion detection, signature and anomaly based techniques and machine learning based techniques for intrusion detection. Intrusion detection and prevention systems performance evaluation, issues related to security and defense and network software tools such as bro, Wireshark and Snort will also be discussed.
Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing [TX6244]
Ethical hacking, or also known as penetration testing, is a disciplined and methodological approach to test a computer security in a computer network, a wireless environment, web applications and online services. In this course, the students can compare, and evaluate the techniques needed for the purpose of ethical hacking and penetration testing specific systems. The students also can demonstrate practical competence in a number of hacking techniques: social engineering, reconnaissance, scanning, enumeration, exploiting Linux and Windows applications, client side attacks, web application attacks, password attacks, and denial of service attacks. Finally, the students can integrate their knowledge and skills into evolving techniques in information security
Security Audit and Assessment [TX6254]
This course introduces the concept of computer system audit and security assessment. It involves techniques in internal audit, and security control in ICT environment, consisting of network, application and operating systems. Students should understand the importance of internal control in an organisation, thus information system auditing. It also discusses audit objectives and procedures for internal controls (management and applications). The use of Computer Assisted Auditing Techniques and Tools (CAATTs) using ACL.
Software Security [TX6234]
This course aims to provide skills and knowledge to produce secure software. It starts with the discussion about possible threats on software and its technical cause. In order to reduce this treats, secure software development lifecycle should be in place, hence a few standard lifecycle are presented. Two important software products that are database and web application will be then thoroughly explored in term of its security. Finally, methods to justify that software product has embedded certain level of security aspect are examined.
Fundamental of Digital Forensics [TD6104]
This course introduces the fundamental of digital forensics domain. It covers introduction to forensic science, basics and management of investigation, quality assurance and countermeasures. Students would also learn the processes of investigation conducted by an investigator officer or first responder in managing and solving contemporary forensic digital problem related to digital evidence. It covers phases of identification, seizure at the crime scene, preservation, analysis and presentation of findings to stakeholders and court. Additionally, this course also explains management digital forensic lab including process of building a forensic laboratory, and the management of people, technology and activities.
Digital Media Forensic Analysis [TD6314]
This course introduces the methods of digital media forensic analysis on digital evidence related to audio, images and videos files. Prior to that, students will learn basic concept about analog and digital signals in the making of the audio, image and video files including techniques in digital media forensics. Then, students will also be able to learn techniques in writing and presenting findings from analysis of specific digital evidence in a group project.
Data Recovery and Analysis [TD6214]
This course introduces the methods of data recovery and digital forensic on data evidence related to computer and embedded systems such as smartphones and Cloud. Prior to that, students will learn basic concept about file system of computer and smartphones, Operating System, File signature and computer architecture. Then, student will also be taught on the techniques of data recovery on computer, memory and latest technology. Nevertheless, the student will be equipped with techniques on analysis of computer, latest devices and technology, writing and presenting findings from analysis of specific digital evidence. Finally, this course will generate expert witness for the forensic cases related to computer, memory and latest technology
Digital Banking and Financial Services [TX6334]
This course aims to provide understanding on the application of technology in banking and other financial institutions. The module begins with a discussion on financial system (conventional & Islamic) components that covers: fundamental and history of financial system, central bank and monetary policy, financial instruments, and determination of financial instruments' pricing. Following that, discussion focus on digital banking system which consists of banking network infrastructure, bank core applications, as well as online banking. The discussion continues with security measures and standard practiced by banking and financial institution to ensure security of the system. Common financial frauds that occur as a result of digital system vulnerabilities are also discussed. The module ends with an exposure of fundamental digital forensic investigation in banking and financial services.
Financial Technology and Risk [TX6344]
Financial technology (FinTech) is a new technology and innovation that aims to make financial services more efficient. This technology covers the areas of big data analytic, online financial services and payment card technology. However, big data analytic will not be covered in this module. The module begins with a discussion on various type of FinTech and its differences. Then, architectures of e-commerce platform with payment gateway and digital wallet, payment card, Secure Electronic Transaction protocol which underpinning the online payment services, blockchain and cryptocurrency will be discussed. The discussion continues with Regulations and standards that FinTech has to comply. After that, students will be challenged to identify security risks in the discussed technology based on accepted security risk management model. Following that, mitigation and control elements that can be applied to manage the risks will be discussed. Throughout the module, real financial crime cases based on the technology vulnerabilities will be used as a case study.
Project I [TX6074]
A project is defined as an effort that involves specific processes. Projects are useful for training students in conducting independent research. Through a project, a student should be able to integrate all knowledge and skills that have been obtained throughout the course of study, in order to complete the research. In order to fulfil research requirements, the student is required to prepare a project proposal that contributes to the chosen area of research. After a project title has been agreed upon with the supervisor, the student will conduct a literature review in order to have an understanding of the current status of the research area. A comparison of past research must be performed and critically analysed. This comparison is done to identify problems that need to be examined in the chosen field of research. This leads to the identification of the research element which must be clearly stated after the literature review stage. The project proposal involves the application of existing techniques in a new domain, data or problem area.
Project II [TX6078]
From the analysis of Project I that has been conducted, a student needs to model a solution to a problem that has been identified and subsequently demonstrate the solution through the implementation of existing techniques in a new domain, data or problem. At the end of the research, the student needs to prepare a report in a UKM style format that elaborates on the problem to be solved, the analysis, the solution model or development of prototypes and experiments that have been conducted.
Programme Schedule
Component Schedule
| Semester | Component |
|---|---|
| Semester 1 |
|
| Semester 2 |
|
Note: This is an ideal schedule for those who want to complete the programme in one year. However, students are given a maximum of 4 years to complete all ApelQ components.
How To Apply
We have two (2) intakes per year :
- September (Semester 1)
- February (Semester 2)
Please apply via online application through MQA Malaysia
Note:
When preparing your CV, please attach one page about your background in cyber security. The template can be found on the ‘DOCUMENT’ page.
Fees
RM24,000 for LOCAL candidate
- Complete program fee is RM24,000 which will be paid in THREE (3) installments (FULL-TIME) on per semester basis :
- 1st Semester : RM9,000
- 2nd Semester : RM7,500
- 3rd Semester : RM7,500
- FOUR (4) installments (PART-TIME) on per semester basis :
- 1st Semester : RM7,200
- 2nd Semester : RM5,600
- 3rd Semester : RM5,600
- 4th Semester : RM5,600
RM32,000 for INTERNATIONAL candidate
- Complete program fee is RM32,000 which will be paid in THREE (3) installments (FULL-TIME/PART-TIME) on per semester basis :
- 1st Semester : RM12,000
- 2nd Semester : RM10,000
- 3rd Semester : RM10,000
FAQ
Am I eligible to apply for this program?
Please check at the Admission Requirement page, where you must have a bachelor degree in the relevant area. Working experiences in the relevant area are considered too.
How much does it cost?
RM24,000 for LOCAL candidate
- Complete program fee is RM24,000 which will be paid in THREE (3) installments (FULL-TIME) on per semester basis (1st Semester : RM9,000 • 2nd Semester : RM7,500 • 3rd Semester : RM7,500) OR
- FOUR (4) installments (PART-TIME) on per semester basis (1st Semester : RM7,200 • 2nd Semester : RM5,600 • 3rd Semester : RM5,600 • 4th Semester : RM5,600)
RM32,000 for INTERNATIONAL candidate
- Complete program fee is RM32,000 which will be paid in THREE (3) installments (FULL-TIME/PART-TIME) on per semester basis (1st Semester : RM12,000 • 2nd Semester : RM10,000 • 3rd Semester : RM10,000)
When is the intake?
We have two (2) intakes per year, September (Semester 1) and February (Semester 2). Please apply via online application system (eSpeed).
Is there any funding or sponsorship that I can apply?
Local candidate can apply for PTPTN or funding through KWSP.
What is the medium of instruction?
We use English
When is our first class?
Student under the February intake will start their class in March meanwhile September intake start in October. Class start from 8.30 am to 5.30 pm. Breakfast, lunch and evening break are provided too.
Document
- Slides :
General Apel.Q at UKM Briefing
| CATEGORY | DOCUMENT | FILLED BY | TIME FRAME |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 : Application |
|
Evaluator | Pre-Semester |
| A2 : Registration |
| Student | Within one week after registration |
|
| Student | ||
| B : Portfolio |
|
Student | Semester 1 |
|
|
Student | ||
|
|
Evaluator | ||
| C : Field Visit and Validation |
|
Student | Semester 1 |
|
|
Evaluator | ||
|
|
Evaluator | ||
| D : Challenge Test |
|
Student | Semester 2 |
|
|
Evaluator | ||
|
|
Student | ||
| E : Capstone Project |
|
Student | Semester 2 |
|
|
Evaluator | ||
|
|
Student | ||
*Note: This documents are used for student who already equip with common functional and generic skills in Cyber Security. The evaluator might prepare a different document to suit students with slightly different background.
Gallery

Any enquiry please contact
-
Prof. Dr. Zarina Shukur
(APEL.Q Coordinator) - zarinashukur@ukm.edu.my
- +6 03 - 8921 6466
- Siti Zulaikha Zamruni
- zulaikhazamruni@ukm.edu.my
- +6 03 - 8921 6077
- Syafiqah Najwa Jamali
- snajwajamali@ukm.edu.my
- +6 03 - 8921 6077




