Page 115 - The-5th-MCAIT2021-eProceeding
P. 115
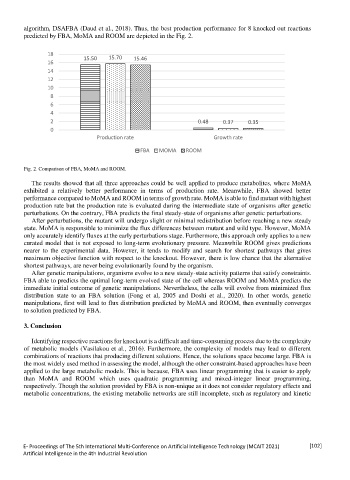
algorithm, DSAFBA (Daud et al., 2018). Thus, the best production performance for 8 knocked out reactions
predicted by FBA, MoMA and ROOM are depicted in the Fig. 2.
18
15.50 15.70 15.46
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2 0.48 0.37 0.35
0
Production rate Growth rate
FBA MOMA ROOM
Fig. 2. Comparison of FBA, MoMA and ROOM.
The results showed that all three approaches could be well applied to produce metabolites, where MoMA
exhibited a relatively better performance in terms of production rate. Meanwhile, FBA showed better
performance compared to MoMA and ROOM in terms of growth rate. MoMA is able to find mutant with highest
production rate but the production rate is evaluated during the intermediate state of organisms after genetic
perturbations. On the contrary, FBA predicts the final steady-state of organisms after genetic perturbations.
After perturbations, the mutant will undergo slight or minimal redistribution before reaching a new steady
state. MoMA is responsible to minimize the flux differences between mutant and wild type. However, MoMA
only accurately identify fluxes at the early perturbations stage. Furthermore, this approach only applies to a new
curated model that is not exposed to long-term evolutionary pressure. Meanwhile ROOM gives predictions
nearer to the experimental data. However, it tends to modify and search for shortest pathways that gives
maximum objective function with respect to the knockout. However, there is low chance that the alternative
shortest pathways, are never being evolutionarily found by the organism.
After genetic manipulations, organisms evolve to a new steady-state activity patterns that satisfy constraints.
FBA able to predicts the optimal long-term evolved state of the cell whereas ROOM and MoMA predicts the
immediate initial outcome of genetic manipulations. Nevertheless, the cells will evolve from minimized flux
distribution state to an FBA solution (Fong et al, 2005 and Doshi et al., 2020). In other words, genetic
manipulations, first will lead to flux distribution predicted by MoMA and ROOM, then eventually converges
to solution predicted by FBA.
3. Conclusion
Identifying respective reactions for knockout is a difficult and time-consuming process due to the complexity
of metabolic models (Vasilakou et al., 2016). Furthermore, the complexity of models may lead to different
combinations of reactions that producing different solutions. Hence, the solutions space become large. FBA is
the most widely used method in assessing the model, although the other constraint-based approaches have been
applied to the large metabolic models. This is because, FBA uses linear programming that is easier to apply
than MoMA and ROOM which uses quadratic programming and mixed-integer linear programming,
respectively. Though the solution provided by FBA is non-unique as it does not consider regulatory effects and
metabolic concentrations, the existing metabolic networks are still incomplete, such as regulatory and kinetic
E- Proceedings of The 5th International Multi-Conference on Artificial Intelligence Technology (MCAIT 2021) [102]
Artificial Intelligence in the 4th Industrial Revolution